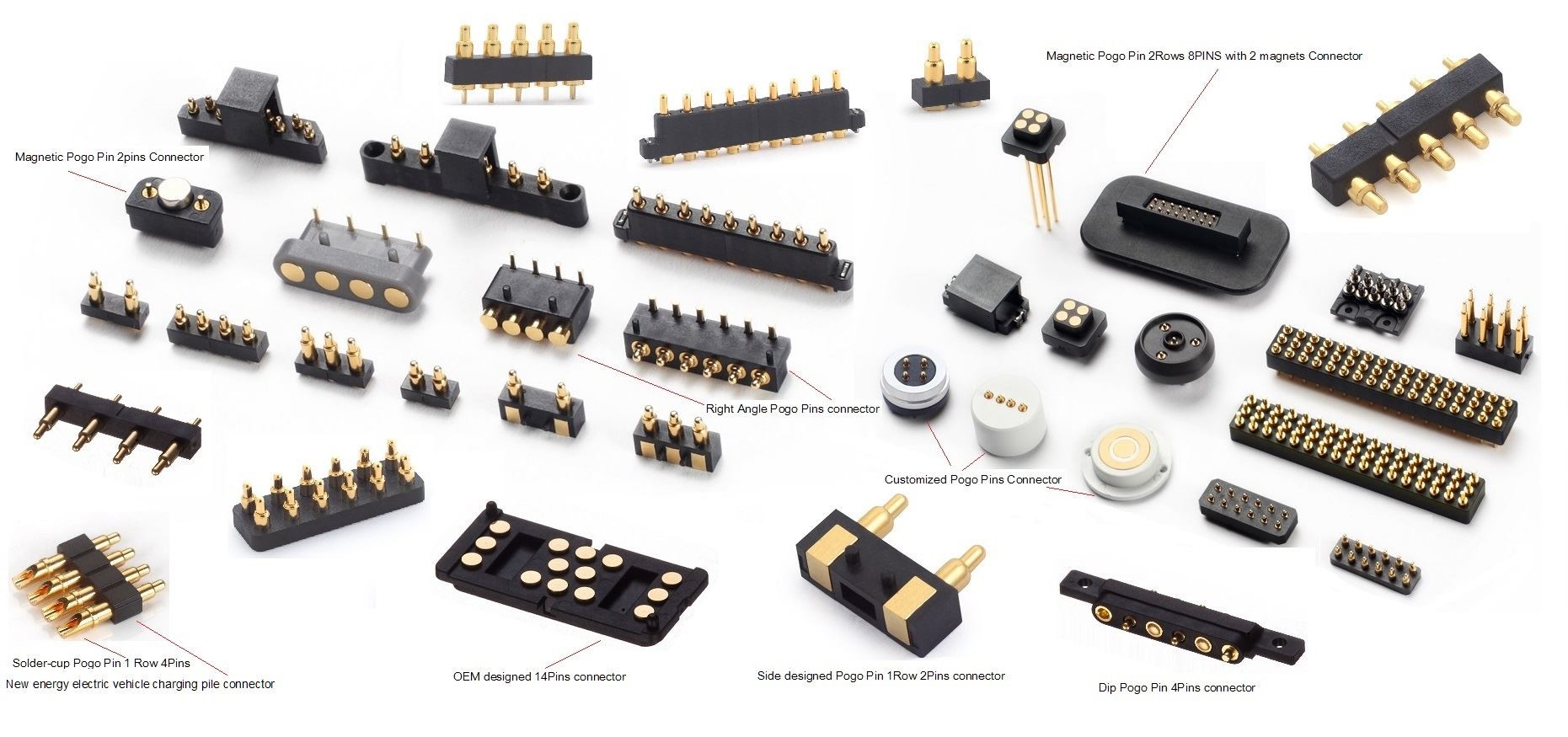
Pogo Pin Connector Production Process

Needle shaft/tube material:
The main function of the connector is that the number of times signal conduction and plugging and unplugging is high, so the conductivity and elasticity (yield strength) of the material are also required.
1-1: Brass (BRASS): copper-zinc alloy, its conductivity is good, the conductivity is about 26%~29% (IACS), according to the proportion of copper can be divided into C2680 (JIS) and C3604, C3601 (required heat treatment)
1-2: Phosphor Bronze (PHOSPHOR BRONZE): copper-tin alloy, its conductivity is worse than brass, the conductivity is about 13%. But its elasticity and flexibility are good
It is suitable for pipes with a drawing process, and its classification can be divided into C5440, C5191, and C5210 according to the tin content. The higher the tin content, the worse the conductivity and the better the elasticity.
1-3: Heat-treated copper alloys: For example, beryllium copper (BERYLLIUM ALLOY) has good electrical conductivity and elasticity, but its price is high.
Materials used for Housing&Cap:
Provide the main structure and insulation of the connector, and accommodate the Pogo PIN inside it. Materials used: The size, shape, and use of connectors are very different, so the engineering plastics used are also various. When designing connectors, temperature resistance, fluidity, mechanical strength, electrical performance, environmental protection requirements, and costs should be considered as Factors to choose the appropriate engineering plastics. Commonly used engineering plastics are LCP, HTN, NYLON46, PBT, PA4T, PA10T, PC, etc.
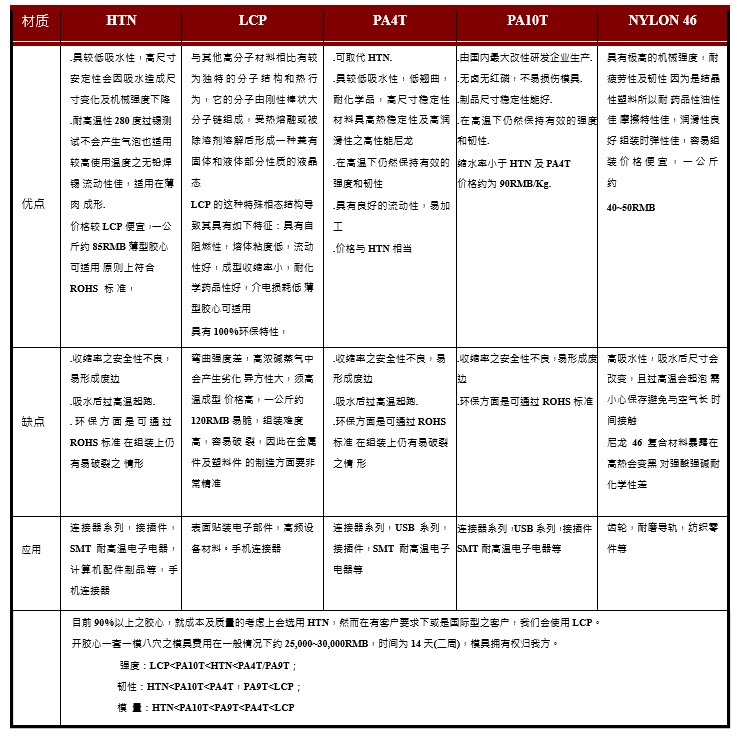
Because LCP itself has flame retardant properties, it can reach UL94 V-0 level without adding flame retardant, so LCP can quickly meet RoHS and halogen-free requirements. HTN, PA4T, and PA9T are nylon materials, and flame retardants need to be added to achieve UL94 V- Class 0, the manufacturers of HTN, PA4T, and PA10T declare that the materials of the relevant grades use halogen-free flame retardants.
